 Asbestos-related diseases
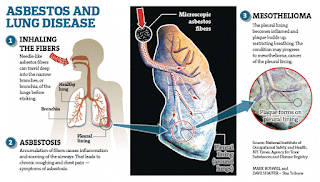
Asbestos-related diseasesRadiografia cell lung asbestos-related risks are caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers, with the smaller ones that reach the lower airways. The length and configuration of the fibers (small size and long, skinny shape) influences their ability to penetrate the airways, as they can remain suspended in the air for a long time and therefore can be inhaled.
Once inside the lungs, the body's defense mechanisms try to break them down and flush them out, being many asbestos fibers that get to stay in the body and remain there for long.
Asbestos is classified according to the Spanish Legislation as carcinogenic top notch, ie "substances known, are carcinogenic to man", therefore it is fully applicable Royal Decree 665/1997 of 12 May on the protection of workers from the risks related to exposure to carcinogens during transvestite link will open in a new window
Occupational disease caused by exposure to asbestos fibers is contained in Royal Decree 1299/2006 This link will open in a window nu-evade November 10, approving the schedule of occupational diseases is approved in the Social Security system and criteria for notification and registration are established, to be
The main health effects from exposure to amphibious area unit pneumoconiosis (pulmonary fibrosis), carcinoma and carcinoma (pleural or peritoneal), association with other malignancies (gastrointestinal or organ carcinomas) having conjointly found. Is suspected, not confirmed, that amphibious will cause different cancers (kidney, ovarian, breast).
Asbestos's
Asbestos is defined as diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis caused by exposure to asbestos dust, which can affect the parenchyma and the visceral and parietal pleura. It is clinically indistinguishable from pulmonary fibrosis caused by the other causes. Sometimes it comes in the form of desquamative interstitial pneumonia (NID), granulation inflammation or lung disease bronchiolitis obliterans organizing (BONO).
The clinical signs and symptoms that often accompany asbestos-is are shortness of breath and coughing, inspiration crackles lung fields and media bases, and clubbing. respiratory functional abnormalities such as impaired alveolar-capillary diffusion and a restrictive pattern may be associated with obstruction may occur. The decrease in pulmonary diffusing capacity is the parameter alters earlier and its deterioration is often even to the evolution of the disease. The impaired lung function can continue even after exposure has ceased and in the absence of radio logical signs of asbestos is, and appears to be dose-response relationship between it and the level of exposure.
Effort dyspepsia is usually the first symptom, although it is late-onset 15-20 years after the start of the exhibition. The cough is non-productive, and not in all cases. In advanced stages it may appear asthenia, hypnosis and symptoms of cor pulmonary.
The pleurae involvement occurs in about 50% of cases of asbestos is. Pleural plaques results, especially the parietal pleura, sometimes calcification- with diffuse pleural thickening sometimes merging both pleura, parietal and visceral (mainly in the lower half of the lungs), benign pleural effusion, flattening angle Costophrenic , pleuroparenquimatosa fibrosis and electorates. It is usually asymptomatic.
malignant mesothelioma
It is a malignant tumor of the mesothelioma diffuse, which can affect the pleura, peritoneum and pericardium, but more often the pleural location. Peritoneal location requires more exposure to asbestos.Amphibious, particularly crocidolite, they show more carcinogenic than Chrysostom power. This seems to be related to the diameter and configuration of the fibers, the crocidolite are small in diameter and length; this would promote penetration of the fibers to achieve the pleura.
Pleural mesothelioma is associated with asbestos is in 25% of cases while peritoneal mesothelioma is often associated with asbestos is, because in these cases to intense exposure to asbestos. The vast majority of mesothelioma's are caused by asbestos exposure (in the 80-85% it is stated occupational exposure). Smoking and the presence of metals or organic substances seem to have no influence on the risk of contracting the disease.
Pleural mesothelioma presents with pleural effusion, dyspepsia and chest pain. It may be accompanied by effusion or pleural thickening.
Lung cancer
Lung cancer from asbestos exposure may be of any scatological type, and its natural history is no different from cancer caused by other causes. There appears to be a dose-response relationship between the risk of lung cancer and asbestos exposure level; very low exposures seem to increase risk. The risk of lung cancer is greatly increased if asbestos exposure combined with smoking.
The attribution of cancer to asbestos is based on the previous history of exposure to this product. minimum latency period of 10 years required. known as asbestos is or pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer and pleural or peritoneal mesothelioma.
Get More